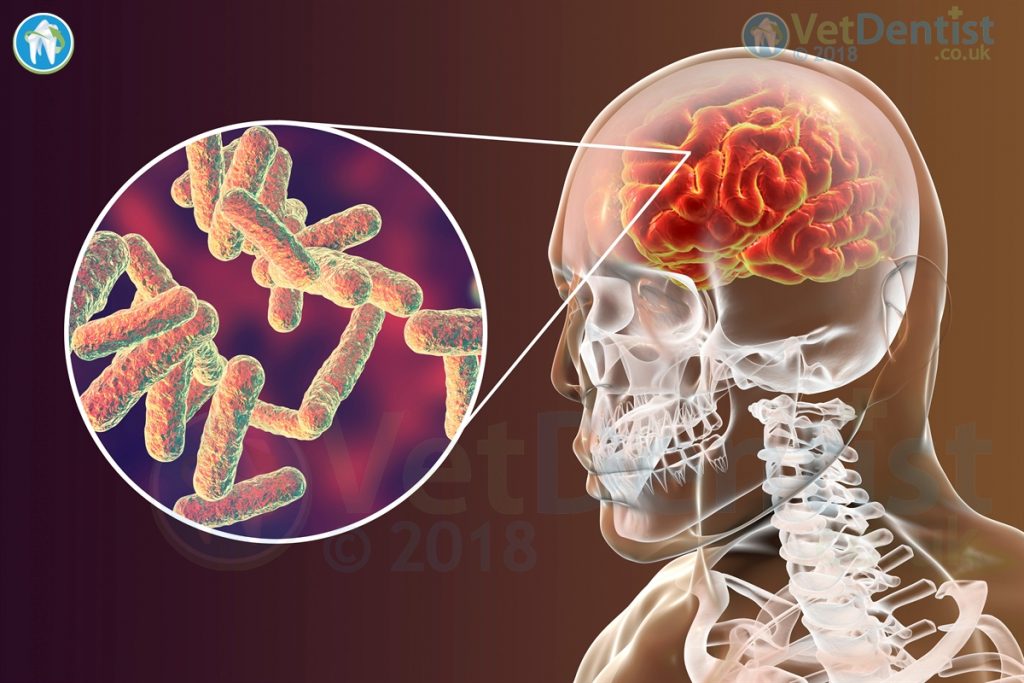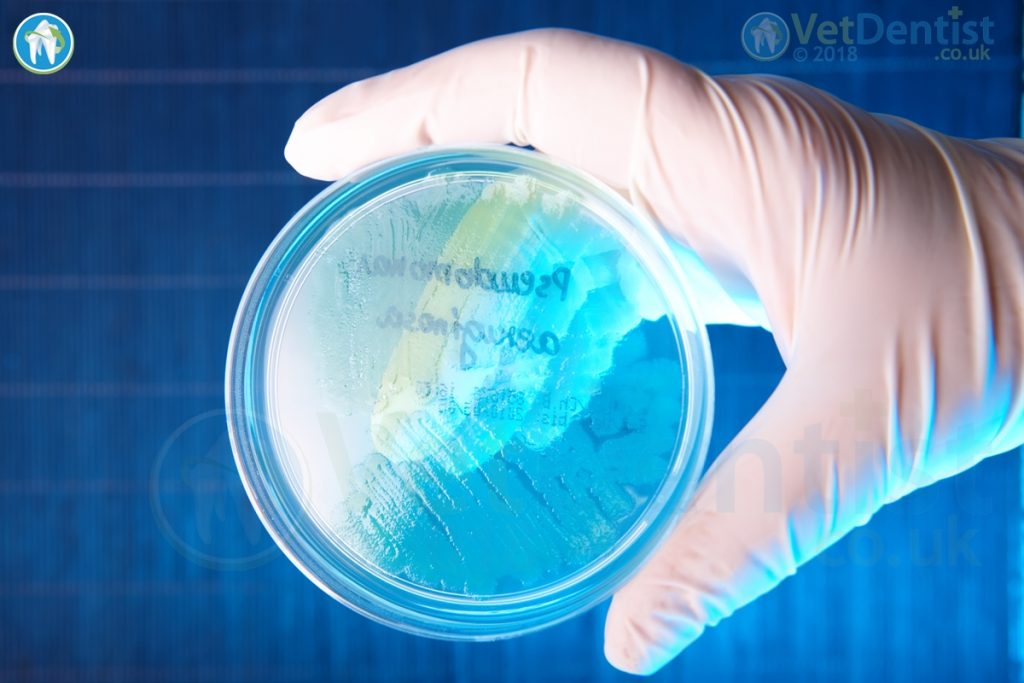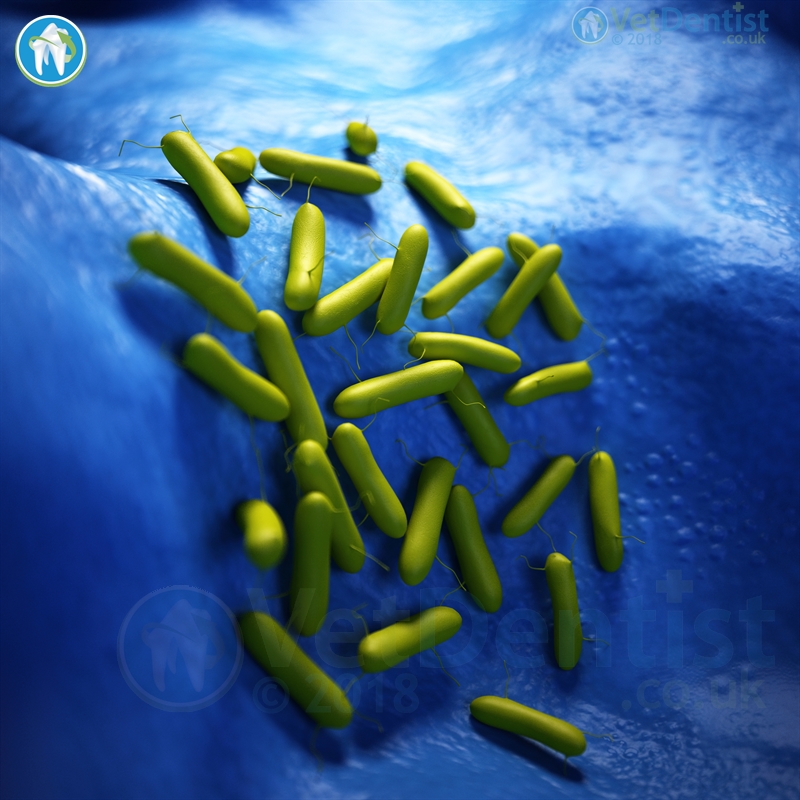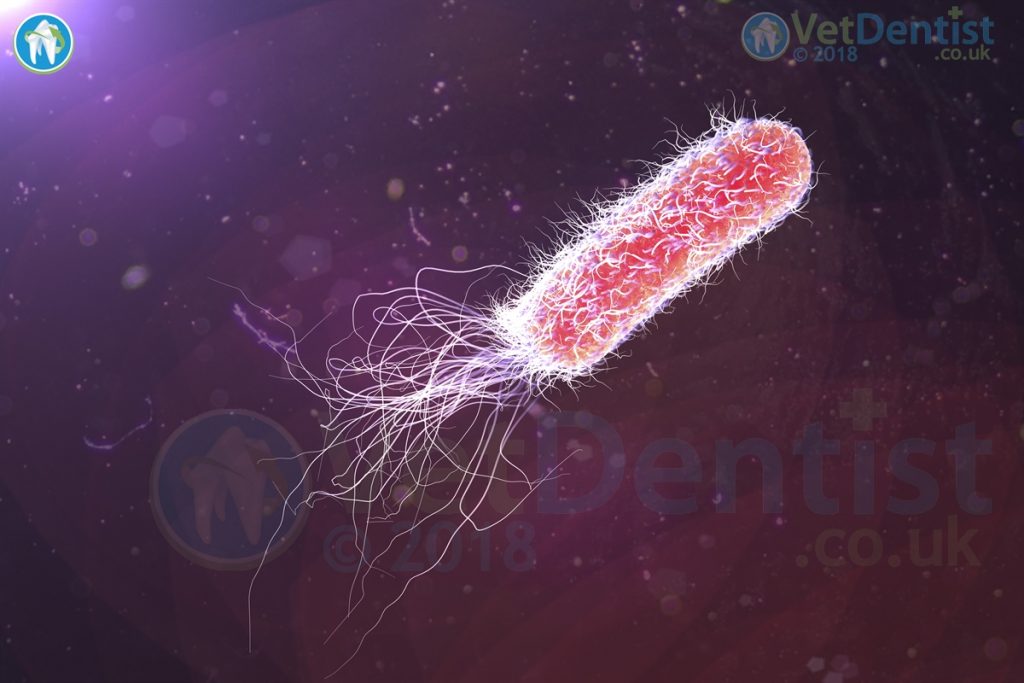
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a highly resistant bacteria. It has the ability to grow even in dilute solutions of chlorhexidine or iodophors. It can also grow in low nutrient environments, even including growing in distilled water! P. aeruginosa also acts to suppress the growth of other organisms, so it becomes the predominating bacteria.
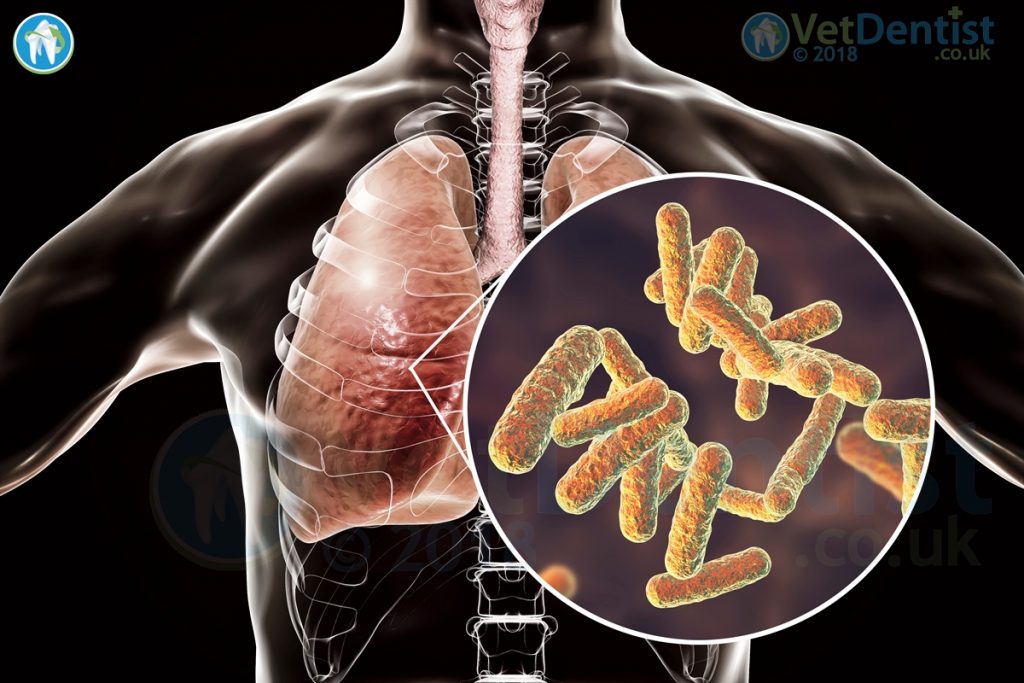
Signs of infection can be very varied, a broad spectrum of problems can arise including pneumonia, septicaemia, and a wide range of soft tissue infections. Treatment can be difficult due to the resistance to a range of common antibacterial agents.
Potential Issues with Dental Units
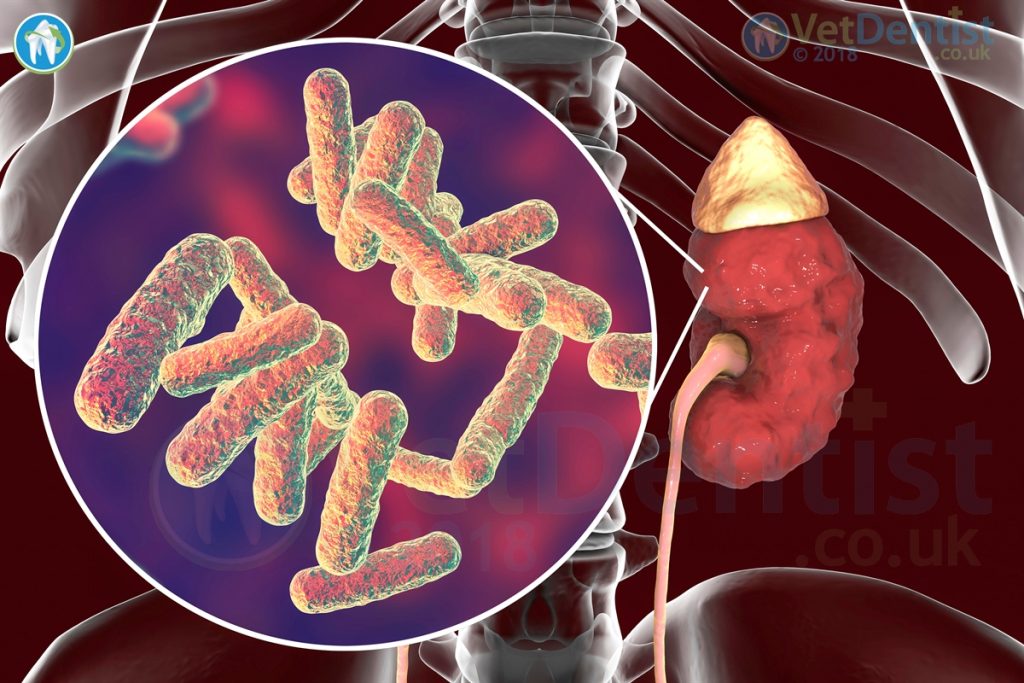
P. aeruginosa was isolated from 24% of Dental unit Water Lines (DUWLS).
Once it was isolated from a particular unit it would frequently be recovered again – despite hygiene measures being taken.
Two oncology patients developed gingival abscesses with a strain of Pseudomonas matching that found in the DUWL used to treat them.
A cystic fibrosis patient developed a pneumonic infection linked to Pseudomonas within the DUWL.